Cool Tips About Is 7 Volts Enough To Start A Car

Can a Wimpy 7 Volts Actually Start Your Car? The Shocking Truth
1. Decoding the Voltage Mystery
Alright, so you're standing there, key in the ignition, and all you hear is... nothing. Maybe a click, maybe a pathetic whimper. Then you grab your voltmeter and it reads 7 volts. Seven! Is that even enough to power a decent flashlight, let alone start a combustion engine beast? Well, settle in, because we're about to dive into the electrical heart of your car and dissect this very voltage-ous question: "Is 7 volts enough to start a car?" Spoiler alert: the answer is probably a resounding NO. But let's understand why.
A car battery isn't just a big, heavy box of chemicals; it's a finely tuned electrical system. It's designed to deliver a specific voltage range to power various components. Think of it like ordering a gourmet burger. You expect a certain level of quality, right? You wouldn't be thrilled if they served you a sad, squashed patty on a stale bun. Similarly, your car expects a healthy dose of voltage to function correctly. Seven volts is more like that sad burger.
The starting process in your car is a complex dance of electricity. The battery needs to have enough juice to power the starter motor, which in turn cranks the engine. This cranking motion pulls air and fuel into the cylinders, preparing them for ignition. Then the spark plugs, also powered by the battery, ignite the mixture. All of this requires a significant amount of power, far more than 7 volts can realistically provide.
Think of it this way: Imagine trying to lift a heavy box with only one working arm. You might be able to wiggle it a little, but you definitely won't get it off the ground. Seven volts attempting to start your car is like that one arm; it lacks the necessary strength to do the job.

What a Healthy Battery Voltage Actually Looks Like
2. Knowing the Right Numbers
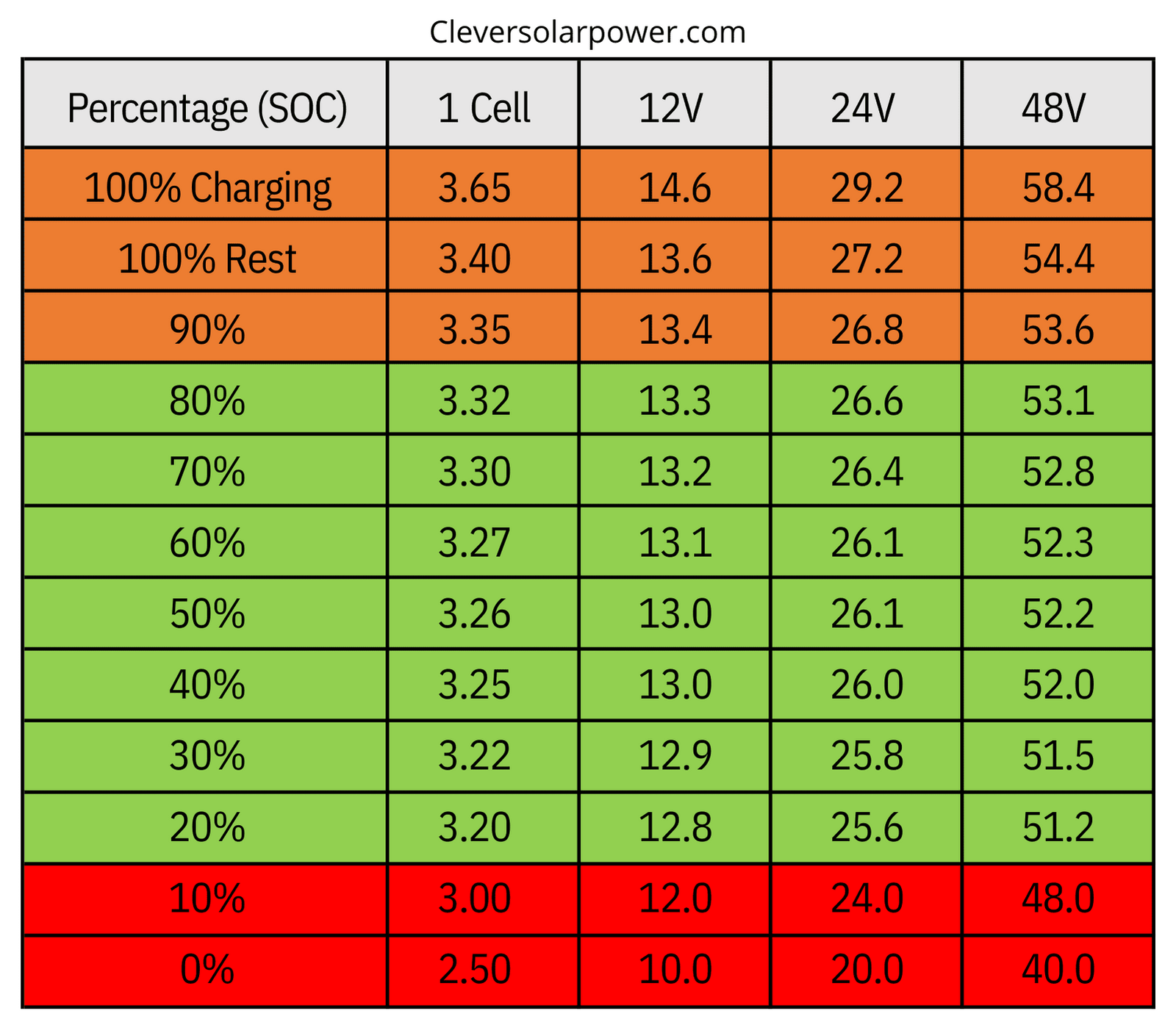
So, if 7 volts is a no-go, what's the sweet spot? A fully charged car battery should ideally sit around 12.6 volts or higher when the engine is off. This is its resting state, like a coiled spring ready to unleash its energy. When you turn the key, the voltage will drop slightly as the starter motor engages, but it should remain above 10 volts during cranking. A drop below 10 volts is a telltale sign of a weak or dying battery.
It's important to note that voltage isn't the only factor. Amperage, which is the rate of electrical flow, also plays a crucial role. A battery with good voltage but low amperage might still struggle to start your car, especially in cold weather when the engine oil is thicker and harder to turn. It's like having a strong arm but no grip; you can't lift anything effectively.
Regularly checking your battery's voltage is a smart habit. You can use a simple multimeter, which is a relatively inexpensive tool that can be found at most auto parts stores. Just connect the red lead to the positive terminal and the black lead to the negative terminal, and the meter will display the voltage reading. Consider it a quick health check for your car's power source.
Furthermore, remember that temperature affects battery performance. Cold weather reduces the chemical reactions inside the battery, making it harder to produce the necessary power. That's why cars often struggle to start on frosty mornings. Conversely, extreme heat can shorten a battery's lifespan over time.

What Is The Voltage Of Car Batteries
Why Your Battery Might Be Showing Only 7 Volts
3. Unraveling the Battery Breakdown
Okay, so you've got a pathetic 7 volts staring back at you from the multimeter. What gives? Several culprits could be at play here. The most common reason is a dead or severely discharged battery. This can happen if you accidentally left your headlights on overnight, or if your car has been sitting unused for an extended period.
Another possibility is a faulty alternator. The alternator is responsible for charging the battery while the engine is running. If it's not working properly, the battery will slowly drain, eventually leading to a low voltage reading. Think of the alternator as the battery's personal trainer; if it's slacking off, the battery will get weak.
Corrosion on the battery terminals can also impede the flow of electricity, resulting in a lower voltage reading. The white, powdery substance that accumulates around the terminals acts as an insulator, preventing the battery from delivering its full potential. Cleaning the terminals with a wire brush and a mixture of baking soda and water can often restore proper conductivity. This is like cleaning a clogged artery to improve blood flow; it allows the electricity to flow more freely.
Finally, internal damage to the battery itself can be the cause. This can be due to age, excessive vibration, or extreme temperatures. In this case, the battery is simply unable to hold a charge, and replacement is the only solution. It's like having a leaky bucket; no matter how much water you pour in, it will eventually drain out.
LiFePO4 Voltage Charts (1 Cell, 12V, 24V, 48V)
Troubleshooting Steps
4. Getting the Juices Flowing Again
Don't despair just yet! If your battery is showing 7 volts, there are a few things you can try before resorting to a full replacement. The first and easiest step is to try jump-starting the car with another vehicle. This will provide a temporary boost of power to get the engine running, allowing the alternator to recharge the battery. Make sure to follow the jump-starting procedure carefully, connecting the cables in the correct order to avoid damaging either vehicle's electrical system. It's like giving your battery a shot of adrenaline to get it going again.
If jump-starting works, let the car run for at least 30 minutes to allow the alternator to recharge the battery. Then, turn off the engine and check the voltage again. If it's still low, the battery might be too far gone to recover fully. Consider taking it to an auto parts store for a load test, which will assess its ability to hold a charge under load. This is like giving your battery a stress test to see how it performs under pressure.
Another option is to use a battery charger to slowly recharge the battery overnight. This is a gentler approach than jump-starting and can sometimes revive a deeply discharged battery. However, if the battery has internal damage, even a full charge might not be enough to restore it to its former glory. Slow charging is more like a recuperative rest cure to try and revitalise it.
Before any attempts at jump-starting or charging, inspect the battery terminals and cables for corrosion or damage. Clean them thoroughly with a wire brush and baking soda solution to ensure a good electrical connection. Replacing corroded cables can also improve the flow of electricity and boost battery performance. This is like making sure all the connections in your electrical system are clean and secure.
When It's Time to Say Goodbye
5. Recognizing the End of the Line
Sometimes, despite your best efforts, a battery is simply beyond repair. If you've tried jump-starting, charging, and cleaning the terminals, and the voltage still refuses to climb above a dismal level, it's likely time for a replacement. Ignoring the signs of a failing battery can lead to inconvenient breakdowns and leave you stranded at the most inopportune moments. It's like ignoring a persistent cough; it might eventually turn into something more serious.
Other telltale signs of a dying battery include slow engine cranking, dimming headlights, and a persistent battery warning light on your dashboard. These symptoms indicate that the battery is struggling to provide the necessary power to operate your car's electrical systems. Pay attention to these warning signs and address them promptly to avoid further problems.
The average lifespan of a car battery is typically between three and five years, although this can vary depending on factors such as climate, driving habits, and battery quality. If your battery is approaching the end of its expected lifespan, it's a good idea to have it tested regularly to assess its condition. Preventative maintenance can save you from unexpected battery failure.
Choosing the right replacement battery is also crucial. Consult your owner's manual or an auto parts professional to determine the correct battery size and type for your vehicle. Consider factors such as cold-cranking amps (CCA), which indicate the battery's ability to start the engine in cold weather, and reserve capacity, which indicates how long the battery can power essential accessories if the alternator fails. Selecting the appropriate battery will ensure optimal performance and reliability.

FAQ
6. Answering Your Burning Questions
Q: My car starts sometimes, but not others. Could it be the battery, even if the voltage seems okay?A: Absolutely! Intermittent starting issues can often point to a weak battery, even if the voltage reading appears within a normal range at times. The battery might have enough voltage to start the car under ideal conditions, but struggle when the engine is cold or when other electrical components are drawing power. Have the battery load-tested to check its ability to deliver sustained power under load.
Q: I jump-started my car, and it's running now. Do I still need to replace the battery?A: Not necessarily, but it's highly recommended to have it checked! A jump-start is a temporary fix. If your battery drained completely, it might have sustained damage that shortens its lifespan. Get a load test to see if it's still holding a charge properly. You might be able to postpone replacement for a bit, but prepare for the possibility of another dead battery in the near future.
Q: Can I revive a completely dead battery by charging it for a long time?A: It depends. If the battery is just deeply discharged, a slow, prolonged charge (using a trickle charger) might bring it back to life. However, if the battery has internal damage (due to age, sulfation, or freezing), charging won't fix the problem. In fact, trying to charge a severely damaged battery can be dangerous. Proceed with caution and monitor the battery closely during the charging process. If it starts to overheat or swell, disconnect it immediately.
Q: What does "cold cranking amps" or CCA mean?A: CCA, or cold cranking amps, is a rating that indicates how many amps a battery can deliver for 30 seconds at 0 degrees Fahrenheit while maintaining at least 7.2 volts. This is critical for starting your car in cold conditions where the engine oil is thicker. More CCA is generally better, especially in colder climates.