Glory Tips About Why Is 3 Phase 380V

Diagram 3phase Ac Motor Why Threephase Voltage Is 440 Volts
Unlocking the Mystery
1. The Backbone of Modern Industry
Ever wonder why industrial power isn't just like the stuff coming out of your wall socket at home? There's a good reason we use 3-phase 380V in factories, commercial buildings, and even some larger homes these days. It's not just some random number they pulled out of a hat; it's a carefully engineered solution to efficiently deliver power to where it's needed most. Think of it as the industrial-strength version of electricity, ready to tackle the heavy lifting that single-phase power just can't handle. Seriously, imagine trying to run a whole manufacturing plant with just standard household voltage. Things would get a bit interesting, to say the least.
The shift to 3-phase 380V boils down to efficiency and capability. Single-phase systems, like what you're used to charging your phone with, deliver power in pulses. Thats fine for smaller devices, but for hefty machinery, you need a smoother, more consistent flow. Three-phase power, on the other hand, delivers power in a more balanced and continuous manner. Imagine three rowers in a boat, each pulling at slightly different times, keeping the boat moving forward smoothly — that's kind of how it works. This leads to reduced energy waste, less vibration in motors, and a longer lifespan for your equipment. Who wouldn't want that?
It's important to note that 380V is more of a regional standard. While it's common in many parts of the world (especially Europe and Asia), you'll find other voltages like 400V or 415V in some locations. The specific voltage is often determined by historical infrastructure and national regulations. So, when someone says "3-phase 380V," they're usually referring to a general class of power distribution systems optimized for industrial and commercial applications in specific regions. In the US, 480V is a common 3-phase voltage instead.
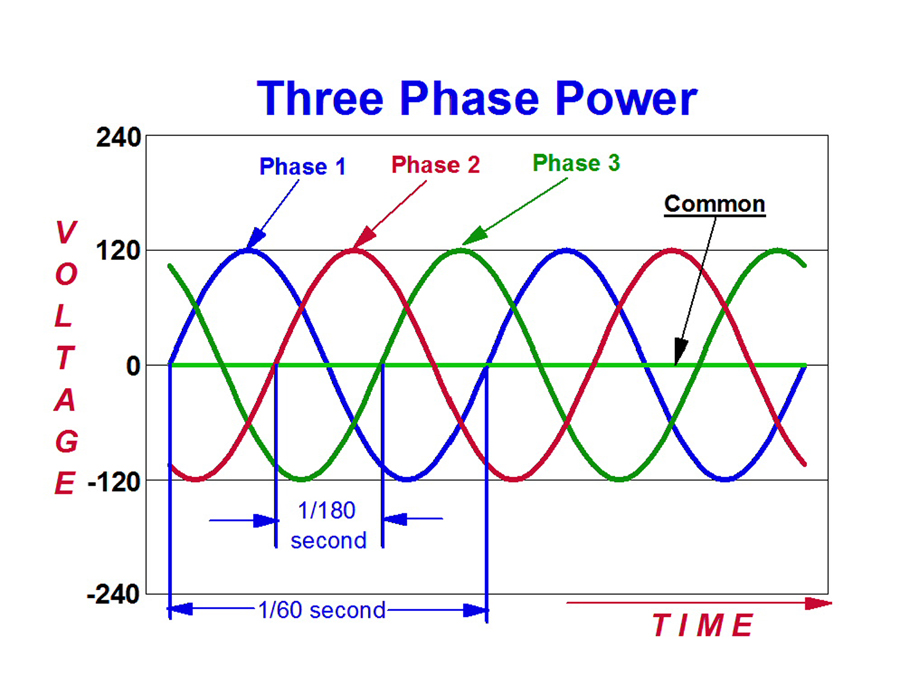
Furthermore, the "3-phase" part refers to the fact that the power is delivered using three separate alternating current (AC) waveforms that are offset from each other by 120 electrical degrees. This clever arrangement allows for a constant and balanced power supply, minimizing dips and surges. So, next time you see some heavy-duty equipment humming along in a factory, remember that it's likely being powered by the magic of 3-phase 380V (or something similar!), working hard to keep things running smoothly.

3 Phase Motor Wiring Low Voltage
Delving Deeper
2. Why Not Just More Single-Phase?
Okay, so we know 3-phase is good, but why not just use a bunch of single-phase circuits instead? Great question! It all comes down to efficiency and cost. Running multiple single-phase lines to achieve the same power delivery as a 3-phase system would require significantly more copper wiring. Think about the sheer amount of material needed! Not only would this be incredibly expensive, but it would also increase the weight and complexity of the electrical infrastructure. No one wants that kind of hassle.
Another key advantage of 3-phase power is its ability to create rotating magnetic fields. This is especially important for electric motors. In a 3-phase motor, the three phases work together to create a smooth, consistent rotating magnetic field that drives the rotor. This results in higher starting torque, smoother operation, and greater efficiency compared to single-phase motors. Think about trying to push a merry-go-round by yourself versus having three friends help you push at different points — much easier with teamwork!
Beyond efficiency, 3-phase systems also offer better voltage regulation. This means that the voltage remains more stable, even under heavy loads. Stable voltage is crucial for sensitive electronic equipment, as voltage fluctuations can cause damage or malfunction. Imagine trying to watch your favorite show with the lights constantly flickering — pretty annoying, right? Well, imagine that happening to delicate machinery in a factory. Not good!
Furthermore, 3-phase systems are inherently more balanced than single-phase systems. This means that the load is distributed more evenly across the three phases, reducing the risk of overloading any one phase. This balanced load distribution also helps to minimize harmonics, which are unwanted electrical frequencies that can cause problems in the electrical grid. So, by using 3-phase power, we're not only making our own lives easier, but we're also helping to keep the power grid healthy and stable.

Understanding The Wiring Diagram For 380V 3 Phase Systems
The Technical Stuff
3. Understanding the Nuts and Volts
Alright, let's talk a little bit about the technical aspects of 3-phase 380V. Don't worry, we'll keep it relatively painless. The "380V" refers to the voltage between any two of the three phases, often called the line-to-line voltage. You might also hear about the line-to-neutral voltage, which is usually around 220V in a 380V system. This is the voltage you'd get if you measured between one of the phases and the neutral wire.
The three phases are typically designated as L1, L2, and L3 (or sometimes A, B, and C). Each phase carries an alternating current that oscillates at a specific frequency, usually 50 Hz or 60 Hz depending on the region. The key is that these three currents are offset from each other by 120 degrees. This offset is what creates the rotating magnetic field we talked about earlier, and it's what makes 3-phase power so efficient.
Another important concept is the difference between a "wye" (or star) connection and a "delta" connection. In a wye connection, the three phases are connected to a common neutral point, forming a "Y" shape. This configuration provides both line-to-line and line-to-neutral voltages. In a delta connection, the three phases are connected in a closed loop, forming a triangle. This configuration only provides line-to-line voltage. The choice between wye and delta depends on the specific application and the desired voltage levels.
And just a quick note on safety: working with 3-phase 380V power can be dangerous if you don't know what you're doing. High voltages and currents can cause serious injury or death. So, if you're not a qualified electrician, it's best to leave it to the professionals. Electricity is a powerful tool, but it needs to be treated with respect. Lets leave playing with high voltage to the experts, shall we?
Blog My AZ Electrician
Where Do You Find 3-Phase 380V?
4. Beyond the Factory Walls
While it's primarily used in industrial settings, 3-phase 380V isn't just for factories. You'll often find it in large commercial buildings, like office towers, shopping malls, and hospitals. These buildings typically have significant power demands for lighting, HVAC systems, elevators, and other equipment. Using 3-phase power allows them to meet these demands efficiently and reliably.
In some cases, you might even find 3-phase power in residential buildings, especially larger homes or apartment complexes. This is often used for powering things like central air conditioning systems, electric vehicle chargers, or other high-power appliances. However, it's less common in residential settings due to the increased cost and complexity of the electrical installation.
Beyond buildings, 3-phase 380V is also used in a variety of other applications, such as powering water pumps, irrigation systems, and even some public transportation systems. Basically, anywhere you need to move a lot of power efficiently, you're likely to find 3-phase power lurking somewhere nearby. Think of it as the unsung hero of modern infrastructure.
It's important to note that the availability of 3-phase power can vary depending on your location. In some areas, it's readily available, while in others it may require a special connection to the power grid. If you're considering installing 3-phase power in your home or business, it's best to consult with a qualified electrician and your local utility company to determine the feasibility and cost.

Real-World Scenarios
5. Examples of its Use
Let's get down to some practical examples. Imagine a large manufacturing plant churning out widgets. Each machine, from the automated assembly lines to the robotic welders, is likely powered by 3-phase 380V. This ensures that everything runs smoothly and efficiently, maximizing production output. Without 3-phase power, the plant would struggle to meet its production targets.
Now, consider a modern data center housing thousands of servers. These servers require a constant and reliable supply of power to keep websites and applications running smoothly. 3-phase 380V provides the necessary power to operate the servers and cooling systems efficiently, preventing downtime and ensuring data integrity. After all, nobody wants their favorite website to suddenly disappear because of a power outage!
Think about a large-scale agricultural operation using electric pumps to irrigate fields. These pumps require a significant amount of power to move water efficiently. 3-phase 380V allows the farmers to irrigate their crops reliably, ensuring a bountiful harvest. It's a vital part of modern agriculture, helping to feed the world. It makes it easy to see the vital part is modern agriculture!
Even smaller businesses can benefit from 3-phase 380V. For example, a car repair shop with multiple lifts and heavy-duty tools might use 3-phase power to operate its equipment efficiently. A commercial bakery with large ovens and mixers would also benefit from the stable and reliable power provided by a 3-phase system. Ultimately, it is important to consider the needs of any business.
FAQs
6. Clearing Up Any Confusion
Still got questions about 3-phase 380V? No problem! Here are a few frequently asked questions to help clear things up:
7. Q
A: Potentially! It depends on your local regulations and your power needs. If you have large power demands, like an electric vehicle charger or a central air conditioning system, it might be worth considering. However, it's generally more common in commercial and industrial settings. Talk to an electrician to explore all your options.
8. Q
A: Yes, it can be. High voltages and currents can cause serious injury or death. Always work with a qualified electrician when dealing with 3-phase power. Never attempt to tamper with electrical equipment unless you are properly trained and authorized. Your safety is more important than saving a few bucks.
9. Q
A: They are very similar and often used interchangeably. The exact voltage can vary slightly depending on the region and local standards. These voltages are considered to be within the same voltage class for practical applications.
10. Q
A: The utilization of 380V in a three-phase power system isn't arbitrary. This voltage level is the result of design choices, regional standards, and historical practices aiming for optimal balance between power delivery efficiency, safety, and equipment design. A complex relationship exists in engineering and standardization.